|
Diaphragm (acoustics), Diaphragms
Diaphragm may refer to: Anatomy * Thoracic diaphragm, a thin sheet of muscle between the thorax and the abdomen * Pelvic diaphragm or pelvic floor, a pelvic structure * Urogenital diaphragm or triangular ligament, a pelvic structure Other * Diaphragm (optics), a stop in the light path of a lens, having an aperture that regulates the amount of light that passes * Diaphragm (acoustics), a thin, semi-rigid membrane that vibrates to produce or transmit sound waves * Diaphragm (birth control), a small rubber dome placed in the vagina to wall off the cervix, thus preventing sperm from entering * Diaphragm (mechanical device), a sheet of a semi-flexible material anchored at its periphery * Diaphragm (structural system), a structural engineering system used to resist lateral loads See also * Diaphragm arch * Diaphragm pump * Diaphragm seal, a membrane that seals an enclosure * Diaphragm shutter, a type of leaf shutter consisting of a number of thin blades in a camera * Diaphragm val ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
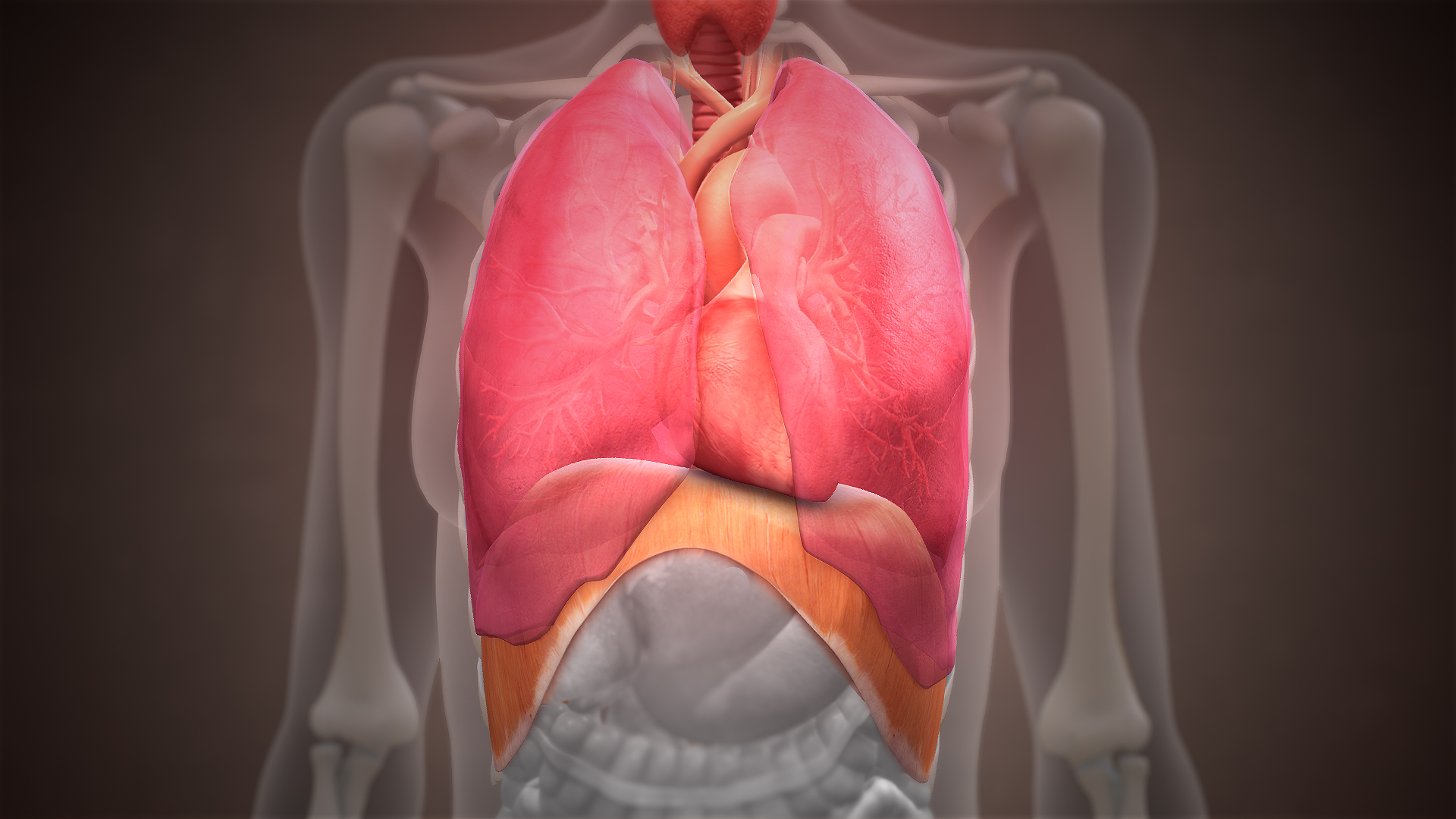
Thoracic Diaphragm
The thoracic diaphragm, or simply the diaphragm (; ), is a sheet of internal Skeletal striated muscle, skeletal muscle in humans and other mammals that extends across the bottom of the thoracic cavity. The diaphragm is the most important Muscles of respiration, muscle of respiration, and separates the thoracic cavity, containing the heart and lungs, from the abdominal cavity: as the diaphragm contracts, the volume of the thoracic cavity increases, creating a negative pressure there, which draws air into the lungs. Its high oxygen consumption is noted by the many mitochondria and capillaries present; more than in any other skeletal muscle. The term ''diaphragm'' in anatomy, created by Gerard of Cremona, can refer to other flat structures such as the urogenital diaphragm or Pelvic floor, pelvic diaphragm, but "the diaphragm" generally refers to the thoracic diaphragm. In humans, the diaphragm is slightly asymmetric—its right half is higher up (superior) to the left half, since th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pelvic Floor
The pelvic floor or pelvic diaphragm is an anatomical location in the human body which has an important role in urinary and anal continence, sexual function, and support of the pelvic organs. The pelvic floor includes muscles, both skeletal and smooth, ligaments, and fascia and separates between the pelvic cavity from above, and the perineum from below. It is formed by the levator ani, levator ani muscle and coccygeus muscle, and associated connective tissue. The pelvic floor has two hiatus (anatomy), hiatuses (gaps): (anteriorly) the urogenital hiatus through which urethra and vagina pass, and (posteriorly) the rectal hiatus through which the anal canal passes. Structure Definition Some sources do not consider "pelvic floor" and "pelvic diaphragm" to be identical, with the "diaphragm" consisting of only the levator ani and coccygeus, while the "floor" also includes the perineal membrane and deep perineal pouch. However, other sources include the fascia as part of the diap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urogenital Diaphragm
Older texts have asserted the existence of a urogenital diaphragm, also called the triangular ligament, which was described as a layer of the pelvis that separates the deep perineal sac from the upper pelvis, lying between the inferior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm (perineal membrane) and superior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm. While this term is used to refer to a layer of the pelvis that separates the deep perineal sac from the upper pelvis, such a discrete border of the sac probably does not exist. While it has no official entry in Terminologia Anatomica, the term is still used occasionally to describe the muscular components of the deep perineal pouch. The urethra and the vagina, though part of the pouch, are usually said to be passing through the urogenital diaphragm, rather than part of the diaphragm itself. Some researchers still assert that such a diaphragm exists, and the term is still used in the literature. The urethral diaphragm is an anatomic landmark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm (optics)
In optics, a diaphragm is a thin opaque structure with an opening ( aperture) at its center. The role of the diaphragm is to ''stop'' the passage of light, except for the light passing through the ''aperture''. Thus it is also called a stop (an aperture stop, if it limits the brightness of light reaching the focal plane, or a field stop or flare stop for other uses of diaphragms in lenses). The diaphragm is placed in the light path of a lens or objective, and the size of the aperture regulates the amount of light that passes through the lens. The centre of the diaphragm's aperture coincides with the optical axis of the lens system. Most modern cameras use a type of adjustable diaphragm known as an iris diaphragm, and often referred to simply as an iris. See the articles on aperture and f-number for the photographic effect and system of quantification of varying the opening in the diaphragm. Iris diaphragms versus other types A natural optical system that has a diaphra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm (acoustics)
In the field of acoustics, a diaphragm is a transducer intended to inter-convert mechanical vibrations to sounds, or vice versa. It is commonly constructed of a thin membrane or sheet of various materials, suspended at its edges. The varying air pressure of sound waves imparts mechanical vibrations to the diaphragm which can then be converted to some other type of signal; examples of this type of diaphragm are found in microphones and the human eardrum. Conversely a diaphragm vibrated by a source of energy beats against the air, creating sound waves. Examples of this type of diaphragm are loudspeaker cones and earphone diaphragms and are found in air horns. Loudspeaker In an electrodynamic loudspeaker, a diaphragm is the thin, semi-rigid membrane attached to the voice coil, which moves in a magnetic gap, vibrating the diaphragm, and producing sound. It can also be called a cone, though not all speaker diaphragms are cone-shaped. Diaphragms are also found in headphones. Qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm (birth Control)
The diaphragm is a barrier method of birth control. It is moderately effective, with a one-year failure rate of around 12% with typical use. It is placed over the cervix with spermicide before sex and left in place for at least six hours after sex. Fitting by a healthcare provider is generally required. Side effects are usually very few. Use may increase the risk of bacterial vaginosis and urinary tract infections. If left in the vagina for more than 24 hours toxic shock syndrome may occur. While use may decrease the risk of sexually transmitted infections, it is not very effective at doing so. There are a number of types of diaphragms with different rim and spring designs. They may be made from latex, silicone, or natural rubber. They work by blocking access to and holding spermicide near the cervix. The diaphragm came into use around 1882. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. Medical use Before inserting or removing a diaphragm, one's ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm (mechanical Device)
In mechanics, a diaphragm is a sheet of a semi-flexible material anchored at its periphery and most often round in shape. It serves either as a barrier between two chambers, moving slightly up into one chamber or down into the other depending on differences in pressure, or as a device that vibrates when certain frequencies are applied to it. A diaphragm pump uses a diaphragm to pump a fluid. A typical design is to have air on one side constantly vary in pressure, with fluid on the other side. The increase and decrease in volume caused by the action of the diaphragm alternately forces fluid out the chamber and draws more fluid in from its source. The action of the diaphragm is very similar to the action of a plunger with the exception that a diaphragm responds to changes in pressure rather than the mechanical force of the shaft. A diaphragm pressure tank is a tank which has pressurant sealed inside on one side of the diaphragm. It is favored in certain applications due to its h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm (structural System)
In structural engineering, a diaphragm is a structural element that transmits lateral loads to the vertical resisting elements of a structure (such as shear walls or frames). Diaphragms are typically horizontal but can be sloped in a gable roof on a wood structure or concrete ramp in a parking garage. The diaphragm forces tend to be transferred to the vertical resisting elements primarily through in- plane shear stress. The most common lateral loads to be resisted are those resulting from wind and earthquake actions, but other lateral loads such as lateral earth pressure or hydrostatic pressure can also be resisted by diaphragm action. The diaphragm of a structure often does double duty as the floor system or roof system in a building, or the deck of a bridge, which simultaneously supports gravity loads. Parts of a diaphragm include: *the collector (or membrane), used as a shear panel to carry in-plane shear *The drag strut member, used to transfer the load to the shear walls ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm Arch
A diaphragm arch is a transverse wall-bearing arch forming a partial wall dividing a vault or a ceiling into compartments while also bracing the walls. When used under a wooden roof (with solid spandrels) it has the advantage of providing a partial firebreak. It was first used in Roman Syria, during the 2nd century AD. The diaphragm arch is present in Islamic, Carolingian, Ottonian and Romanesque architecture. See also * Islamic architecture * Romanesque architecture Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of medieval Europe that was predominant in the 11th and 12th centuries. The style eventually developed into the Gothic style with the shape of the arches providing a simple distinction: the Ro ... * Kucheh References Sources * Arches and vaults {{Architecturalelement-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm Pump
A diaphragm pump (also known as a Membrane pump) is a positive displacement pump that uses a combination of the reciprocating action of a rubber, thermoplastic or teflon diaphragm and suitable valves on either side of the diaphragm (check valve, butterfly valves, flap valves, or any other form of shut-off valves) to pump a fluid. There are three main types of diaphragm pumps: * Those in which the diaphragm is sealed with one side in the fluid to be pumped, and the other in air or hydraulic fluid. The diaphragm is flexed, causing the volume of the pump chamber to increase and decrease. A pair of non-return check valves prevent reverse flow of the fluid. * Those employing volumetric positive displacement where the prime mover of the diaphragm is electro-mechanical, working through a crank or geared motor drive, or purely mechanical, such as with a lever or handle. This method flexes the diaphragm through simple mechanical action, and one side of the diaphragm is open to air. * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm Seal
In mechanical engineering, a diaphragm seal is a flexible substance that seals and isolates an enclosure. The flexible nature of this seal allows pressure effects to cross the barrier but not the material being contained. Common uses for diaphragm seals are to protect pressure sensors from the fluid whose pressure is being measured. Materials Since diaphragm seals need to be highly flexible, elastomers are commonly used, and include a wide variety of both general purpose and speciality rubbers. Elastomers are limited to low pressure applications and those that are chemically compatible with the various plastics and rubbers used. Metal diaphragms of stainless steel (several grades), Carpenter 20, Hastelloy, Monel, Inconel, tantalum, titanium and several other metals are in common use where high pressure ratings and specific chemical compatibility are required. Flanged assemblies or flush welded versions are available. Depending on the PSI levels of the sealing application, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diaphragm Shutter
In photography, a shutter is a device that allows light to pass for a determined period, exposing photographic film or a photosensitive digital sensor to light in order to capture a permanent image of a scene. A shutter can also be used to allow pulses of light to pass outwards, as seen in a movie projector or a signal lamp. A shutter of variable speed is used to control exposure time of the film. The shutter is constructed so that it automatically closes after a certain required time interval. The speed of the shutter is controlled either automatically by the camera based on the overall settings of the camera, manually through digital settings, or manually by a ring outside the camera on which various timings are marked. Camera shutter Camera shutters can be fitted in several positions: * Leaf shutters are usually fitted within a lens assembly (''central shutter''), or more rarely immediately behind (''behind-the-lens shutter'') or, even more rarely, in front of a lens, and shut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |